DeepDDM: A Compact Deep-Learning Assisted Platform for Micro-Rheological Assessment of Micro-Volume Fluids
📌 Research Abstract
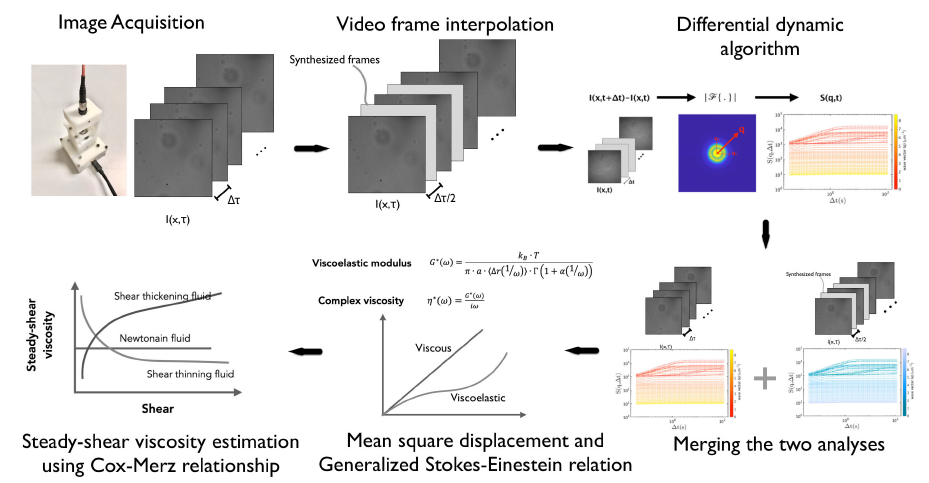
An emerging differential dynamic microscopy technique has been successfully used for quantitative dynamic investigation of micro-particle suspension, leading to a rheological assessment of the solution. This technique exploits an optical microscope equipped with a digital camera for the assessment. However, the accessible measurement ranges at high frequencies are limited by the video frame rate of the camera, resulting in a limitation in investigating distinguish responses at the high-frequency region. With advanced deep learning technology, image-synthesizing deep learning-based algorithms can significantly increase the video frame rate, producing additional in-between frames. As a result, the rheological responses at the high-frequency region can be obtained. To address this problem, a video frame interpolation integrated differential dynamic microscopy-based device (DeepDDM platform) was developed. Our DeepDDM platform interpolates video frames to extend the maximum measuring angular frequency up to quadruple from 30.1 rad/s to 123.0 rad/s, resulting in a more comprehensive rheological assessment without hardware modification. Unlike reducing the camera exposure time approach, our approach requires only a single camera and works without brightness reduction. Furthermore, the device is compact and portable. It comprises a few main components, and requires only 8μL sample volumes for the rheological assessment. Thus, it is easy to relocate to measure biological samples which are often do not retain their natural properties in a storage allowing for in situ studies of the fluids. In comparison, the obtained responses agreed with the reference mechanical rheometer, although the employed partially coherent source and out-of-focus image acquisition bring difficulties to our system.
The website template was borrowed from Michaël Gharbi.




